Israel Adaptation:
As was described in my last post, with the change in the climate, many countries are being affected including Israel. The main threats towards Israel are that there is going to continue to be an increase in temperature and decrease in precipitation. Israel has released a report describing the climate change that has taken affect and future climate predictions for the country. In this report they also overview actions that can be taken in order to adapt to the changes that may occur. The report talks about two different levels of adaptation. Those two levels are: “reaction by precursory actions, in anticipation of change (such as building planning and disaster insurance), and reaction to the change itself (such as migration from disaster areas, coastal nourishment, and enforcement of building regulations)” (Israel’s Second National Communication on Climate Change). There are two adaptation plans that I found to be very interesting. The first deals with Israel’s lack of fresh water and how this amount of fresh water will continue to decrease. The whole entire Western border of Israel is almost completely covered by the Mediterranean Sea. With all of this water available to use by the country, they have decided to find a way to make the water fresh for drinking and watering crops. One way to do this is by desalinating the water to get rid of all of the salt and make it clean for humans and plants. Israel is currently using the desalination process to provide 7 percent of the countries fresh water. While this is not a large percentage, with a decrease in availability of fresh water, they plan on creating more desalination plants in order to adapt to these changes. In fact by 2020, the country plans on increasing the amount of water from desalination plants to a capacity of 35 percent of the total water. Another problem that climate change will bring to Israel is the demand for more air conditioning. As the temperature increases, especially during the summer, the buildings in cities will need to stay cooler in order to keep people comfortable. A couple ideas that were produced are to use the heats source as an energy source and to change the infrastructure of the buildings. Since heat comes from the sun, the production and use of solar panels in order to run air conditioning systems could be a great way to adapt. Solar panels have become much more popular in recent years and this could be a definite solution for the change in the climate. Also buildings could change their structures and insulation to keep them cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter without using electrical sources such as air conditioning and heating. These two examples are just a couple ideas that Israel has come up with to adapt to the changes that will be occurring. They have many other ideas to help with this change which can be found in their report titled Israel’s Second National Communication on Climate Change.
Mediterranean Region Adaptation:
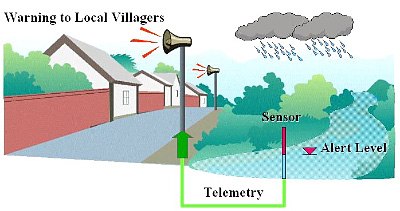
Along the Mediterranean Sea, these countries all have to deal with the problems associated with climate change. One major problem that has to be dealt with being along the coast of a large body of water is flooding. Not only is sea level expected to rise but major weather extremes are supposed to be on the rise as well. Sea level rise mixed with flooding is not the ideal conditions that people want to see. In order to deal with flooding, the Mediterranean region has come with ways to adapt. Since these weather extremes cannot completely be stopped, the ideas that have been suggested are more in the line of protecting humans by helping them avoid flood areas. One strategy is to develop public flood warning systems. With a system like this in place, warnings can be sent out before big storms in order to give people more time to evacuate lower lying areas and areas that are near the coast line. These warning systems will hopefully help save lives when major weather extremes occur. Although it is not easy to prevent sea level rise and flooding, it is possible to adapt by warning humans of oncoming weather.
Kyoto Protocol:
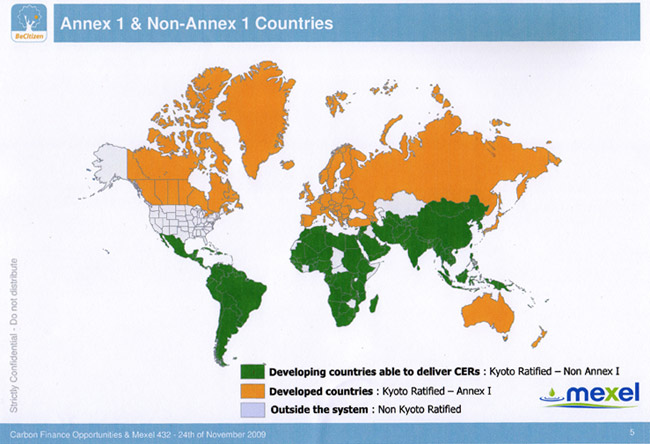
The Kyoto Protocol is an international agreement dedicated to reducing the impacts that humans have on climate change. The focus of this protocol is to give countries a limit of how much carbon they are allowed to emit. Each country has a goal that they will try to meet in order to slow climate change to a more natural pattern. While the Kyoto Protocol is not required for countries to approve, many of them have agreed to accept it. Israel was one of the countries to immediately choose to approve of its ratification. Israel had big goals when this protocol came out because they felt that it was a huge step in helping decrease the affect of climate change. Since Israel is not a large country, their affect on global climate change is not very large, so they had no requirements when it came to making an immediate carbon emissions cut. Even with no requirements, Israel set goals for themselves and is still sticking with the protocol today.
Israel Mitigation:
Although it is not a requirement for Israel to make any changes or reduce emissions coming from their country, they feel that if they do so, it can help change the world and prepare for the upcoming climate changes. Israel plans on reducing emissions by 20 percent by the year 2020. They are going to make this happen by changing the amount of emissions allowed in different split sectors of their country. The different sectors include energy and manufacturing, transport, residential and commercial, waste and wastewater, agriculture, and land use and forestry. Some of the main changes that Israel has made and is planning on making in the near future will now be discussed. First of all, Israel has just recently began using natural gas as a form of energy. By doing this, they are reducing CO2 emissions greatly instead of using other forms of energy. They have also started using solar energy as well as wind energy. In the residential sectors, it is required that solar energy is used for water heating systems. Also, there are two solar thermal power plants in the Negev desert. For wind power, Israel has wind turbines set up in the higher altitude areas of the country. Two of these turbine farms are in the Golan Heights and the Gilboa Mountains. While many of these new practices can get on the higher pricing end, the economic incentives have been taken into account. Israel has research groups that figure out the price of each of these mitigation and adaptation practices and decide whether or not it would be worth putting into action or not. These people research the cost and benefits of each and if the price is not worth the pay off in the end, then they decide against it. In order to motivate the culture and society of Israel to make these changes, there is a plan to give, “exposure of relevant data through public reports to enable a better understanding of the issue, that will build heightened awareness and will enhance personal commitment and action.” (Israel’s Second National Communication on Climate Change) By making the public more aware of the dangers and changes that are in the future, it will motivate the citizens to want to get involved and agree to the mitigation actions that are planned. While Israel is a very small country and it would seem like any changes they make would not make a difference in the world, they are surprisingly very concerned about mitigation. The cultural feel of Israel is to treat their country and land in a way that helps the environment and keeps the atmosphere clean. By making some small changes and mitigating, the affect of climate change on Israel will hopefully not be as bad as expected.
Mitigate or Adapt?
I personally believe that there are pluses and minuses to both mitigating and adapting. While mitigation can help lessen the effect of climate change, it can also be very expensive. Adapting to climate change after it happens can be helpful and necessary, but it may be too late and certain problems may arise like plant and animal life not being able to adapt to the changes and dying out. Since these both have problems, I think the best way to deal with climate change is by including a little of both. The country of Israel can add certain changes to mitigate before the effects are too big to handle. They can change the amount of emissions by driving more fuel efficient cars that do not hurt the environment as much, use different energy sources, and even just put restrictions on emissions for people living in the country. In order to save on costs, research can be done that will show what are the best mitigation strategies that will be the least expensive. This will probably save money in the end anyways because the country won’t have to adapt as much. Once the changes start to occur, the problems that mitigation did not stop can be adapted to. By using both mitigation and adaptation, Israel can prepare for climate change and the problems that come along with it and then adapt to the things that occur.
(All information was obtained from Israel’s Second National Communication on Climate Change Report, the IPCC website, and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change website)